mirror of https://github.com/01-edu/public.git
You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
1.5 KiB
1.5 KiB
insertion_sort
Instructions
The insertion sort algorithm:
- To sort an array of size n in ascending order:
-
Iterate from slice[1] to slice[n] over the slice.
-
Compare the current element (key) to its predecessor.
-
If the key element is smaller than its predecessor, compare it to the elements before. Move the greater elements one position up to make space for the swapped element.
Here is a visual example of sorting a slice step by step using the insertion sort algorithm.
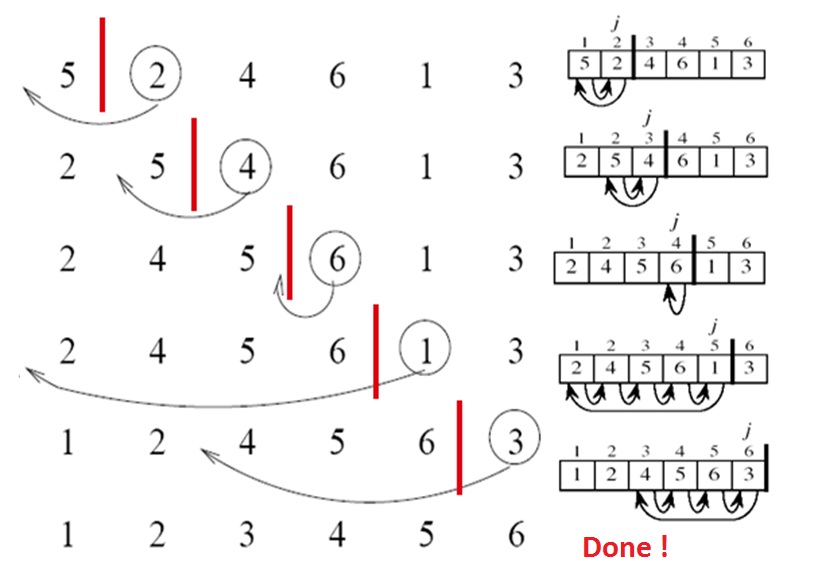 Figure 1 - Step by step execution of the algorithm insertion sort
Figure 1 - Step by step execution of the algorithm insertion sort
- Implement the algorithm insertion sort by creating a function
insertion_sort(slice, steps)that executes the iterations of the algorithm the number of steps indicated by the parametersteps. See the Usage for more information.
Expected Function
pub fn insertion_sort(slice: &mut [i32], steps: usize) {
}
Usage
Here is a possible program to test your function
fn main() {
let mut target = [5, 3, 7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4];
// executes the first iteration of the algorithm
insertion_sort(&mut target, 1);
println!("{:?}", target);
let mut target = [5, 3, 7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4];
let len = target.len();
// executes len - 1 iterations of the algorithm
// i.e. sorts the slice
insertion_sort(&mut target, len - 1);
println!("{:?}", target);
}
And it's output:
student@ubuntu:~/[[ROOT]]/test$ cargo run
[3, 5, 7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
student@ubuntu:~/[[ROOT]]/test$