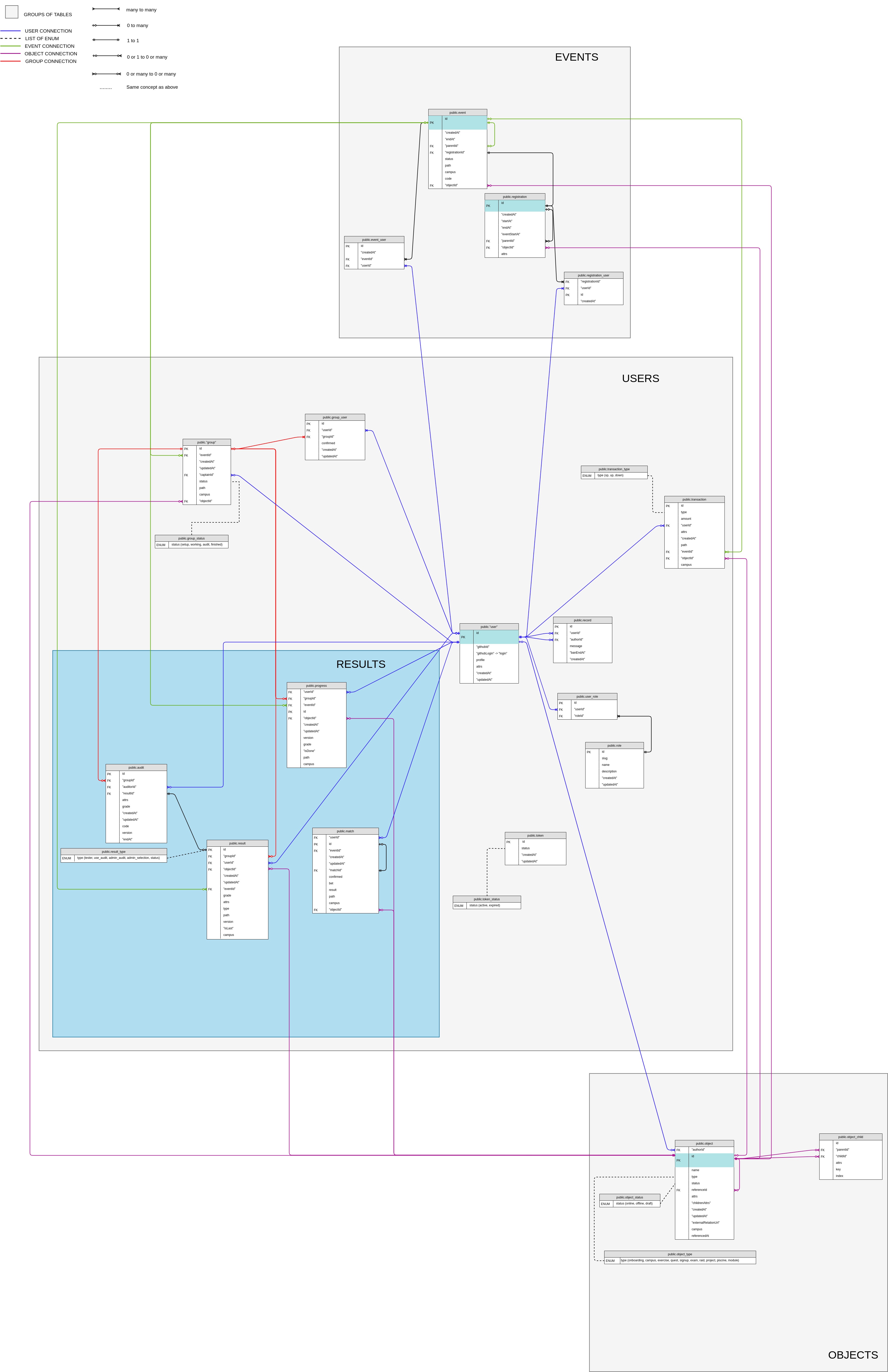
8.8 KiB
Database Relations
Entity Relationship Diagram ERD
An entity relationship diagram (ERD) shows the relationships of entity and sets stored in a database.
An entity in this context is a table, this table contains a set of attributes, they can be of any data structure (INT, TEXT, ...).
An entity can have several relations to other entities. Those relations are represented with "crow foots"
Relationships cardinality
Relationships have a cardinality, normally they have two indicators that are shown on both sides of the line.
-
One end of the line, refers to the max number of times that an instance of one entity can be associated with instances in the related entity. It can be one, many or none
-
The second, describes the min number of times one instance can be related to others. It can be zero or mandatory
The combination of those two indicators create relations, you can get more information here
Relations
Events
Events will be the accumulation of the following tables :
eventregistrationregistration_userevent_user
This part of the database takes care of schools activities with time.
The event table contains the following relations:
-
parentIdthat is associated to himself. This association can be better explained if we take a look at thepathcolumn. An event can be based on a parent event (ex: the event/madere/div-01/piscine-rustis associated to this parent event/madere/div-01). -
registrationIdthat is associated to theregistrationtable. This is a one to one relations, meaning that an event must always have a registration associated to it. -
objectIdthat is associated to theobjecttable, this column will identify which object is associated to which event. An object can have multiple events, but an event must always be associated to an object. (it will never exist an event where theobjectIdisnull)
The event_user contains the associations between events and users. This will contain information on which users are registered to which event. An event can have multiple users and a user can have multiple events, this way being a many to many relationship.
The registration table contains all objects/activities that need registration. Having the following relations:
parentIdthat is associated to himself. As said above (in the events), it has the same use.objectIdthat is associated to the object table, this is the object reference to the registrations.
The registration_user table is a relationship many to many between registration and user. This table contains all users that are registered to an event.
registrationIda registration can have multiple users.userIda user can have multiple registrations.
Objects
Object will be the accumulation of the following tables :
objectobject_childobject_statusobject_type
This part of the database defines the structure of the content.
The object table contains the following relations:
referenceIdthat is associated to himself, this attribute allows the duplication of reference objects (given by 01-edu), that are used to set up campusesauthorIdthat is associated to the user table and this is the author of that object/content.
The object_child table contains the encapsulation of objects. An object can have multiple children and a child must have one object parent. Note that one parent can't be associated two times to children with the same key. This table contains the following relationships to the object table:
parentIdthat associates the parent object to the child object.childIdthat belongs to the parent object.
Both child and parent must have at least one association to the object table, and the object table can have multiple relations with the object_child table.
Example:
Campus madeira is a parent object of piscine-go, therefore the later one is the child.
But piscine-go can be the parent object of all the quest, exams and raids (those being the child objects). And so on... creating a finite cycle.
Users
Users will be the accumulation of the following tables:
roleuser_roleusergroupgroup_usertokenrecordtransaction
The role table contains permission roles for each user.
The user_role contains information on which users are associated to which role. A user can have multiple roles and a role can be associated to multiple users.
The group table is the link between projects or raids and a group of users. This table contains the following relations:
eventIdthat associates which group is related to which event.captainIdthat associates the captain's user.objectIdthat associates which group is related to which object.
The group_user table contains the relation between groups and users. A group can have several users and so do the users.
The token table stores the tokens ids from the hasura authorization variables for each user. This table has no relation between other tables.
The record table takes care of students records (bans). All relations in this table are with the table user.
The transaction table takes care of rewarding the user, by accumulating the user's xp , up and down (you can see more information about those types in the database-structure.md). This table contains the following relations:
userIdthat represents the user rewardedeventIdthat associates the event in which the user was rewarded. Example: the user can be rewarded for an exercise/madere/piscine-go/quest-01/make-it-betterand the parent event of that exercise will be/madere/piscine-go.objectIdthat associates the object in which the user was rewarded. Example: if a user passes an exercise (object), the reward will be associated to that object.
Results
Results will be the accumulation of the following tables:
auditmatchprogressresult
This part of the database defines the users/students progress in the school.
The audit table contains all information related to the audit system and it is one of the ways of obtaining results. This table contains the following relations:
groupIdthat associates the group being audited.auditorIdas the name says, it is linked to the user table and has a relation of many to one. This column will be the auditor.resultIdthat associates the audit to the result. An audit can have one or no results (pending on the auditor review). While the results must have at least one audit.
The match table is another way of obtaining a result. This table is used in bonus exercises to match two students. The following relations are established:
userIdthis will be the user wanting the match to happen.matchIdthis is a self related id, a match can be made by matching other students or it can be none. If the latter is none it means that the student is waiting for the match, otherwise it is a match.eventIdthat associates the event to the current match. Example: a user can be waiting for the exercise/madere/piscine-go/quest-01/teacherthat is located in the/madere/piscine-goevent.objectIdthat associates the object to the current match, this being the bonus exercise that the user is doing.
The progress table is the reflection of user's activity on specific path: registration to an event related, commitment to a group associated to this path, generation of result expected to validate a progress on this path.
userIdthat associates an user with a progress. A progress must always have a user associate to it and a user can or cannot have multiple progresses.groupIdthis association allows each user form a group to have progress. This is a many to none or one connection, meaning that a progress can have none or one group and a group can have multiple progresses.eventIdthat associates which event the user has progressed on.objectIdthat associates which object the user has progressed on.versionis the association between theprogressand theresulttable
The result table keeps the track of students result. The following relations are established:
userIdthat associates an user with a result. An user can have multiple results but a result is associated to just one user.groupIdthat associates a group with a result. The same logic as in theuserIdobjectIdthat associates an object with a result. A result must have always a object associated to it and an object can have multiple resultseventIdthat associates an event with a result. The same logic as in theobjectId