forked from root/public
You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
|
|
3 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| Insertion-Sort-demo.png | 3 years ago | |
| README.md | 3 years ago | |
README.md
insertion_sort
Instructions
- Implement the insertion sort algorithm by creating a function
insertion_sort(slice, steps)which executes the iterations of the algorithm up to the number of steps indicated by the parametersteps. See the Usage for more information.
The insertion sort algorithm to sort an array of size n in ascending order:
-
Iterates from slice[1] to slice[n] over the slice.
-
Compares the current element (key) to its predecessor.
-
If the key element is smaller than its predecessor, compares it to the elements before. Move the greater elements one position up to make space for the swapped element.
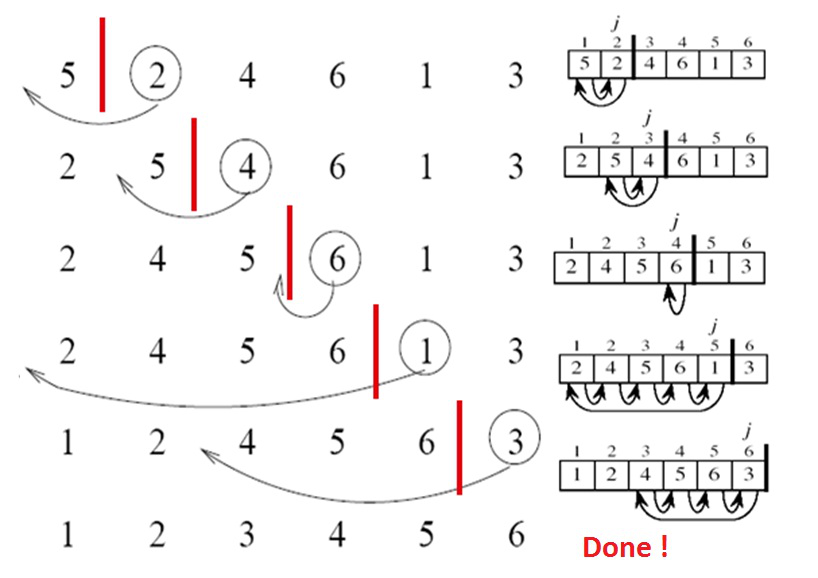
Here is a visual example of sorting a slice step by step using the insertion sort algorithm.
Figure 1 - Step by step execution of the algorithm insertion sort
Expected Function
pub fn insertion_sort(slice: &mut [i32], steps: usize) {
}
Usage
Here is a possible program to test your function,
fn main() {
let mut target = [5, 3, 7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4];
// executes the first iteration of the algorithm
insertion_sort(&mut target, 1);
println!("{:?}", target);
let mut target = [5, 3, 7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4];
let len = target.len();
// executes len - 1 iterations of the algorithm
// i.e. sorts the slice
insertion_sort(&mut target, len - 1);
println!("{:?}", target);
}
And its output:
student@ubuntu:~/insertion_sort/test$ cargo run
[3, 5, 7, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
student@ubuntu:~/insertion_sort/test$