3.0 KiB
DB authorization
Every request to Hasura executes against a set of session variables. These variables are expected to be set by the authentication system.
Normally there are some main variables for the authorization context:
-
X-Hasura-User-Id: this variable usually denotes the user executing the request. -
X-Hasura-Role: This variable denotes the role with which the user is executing the current request. Hasura has a built-in notion of a role, and will explicitly look for this variable to infer the role. -
X-Hasura-campus: this variable contains the campus that the user currently is on.
In our database we have several roles which are simple arbitrary names.
Each role can be given a set of permissions and actions (select, insert, update, delete). That will execute against each table of the database.
To give the user with a certain role a permission to make a request, we must set a permission rule that would look something like this:
{"user_id": {"_eq": "X-Hasura-User-Id"}}
This is the same as saying : if the value of the user_id column equals the value of the session variable X-Hasura-User-Id, allow this request to execute on the current row.
It is possible to express pretty complex rules, by using, for example the operators _and and _or to create a chain rule. It is even possible to query tables not related to the current object as part of the rule execution. You can see more about it here.
Roles
These are the roles presented in the database:
-
anonymous: this role allows non logged in users to query (only usingselect) tables:users: and columnsid,loginobject: and columnsid,childAttr,campus,name,typeresult: and columnsgroupId,objectId,progressId,userId,grade,campustransactions: and columnsobjectId,userId,amount,typeprogress: and columnsisDone,objectId,userId,id,grade,campus
-
user: this role allows the following queries:-
without check:
group,group_user,match,registration_user,event,event_user,object,object_child,object_status,object_type,registration,role,transaction_type
-
with checks:
audit,result,transaction,user_role,user,progress
-
-
campus-admin: this role allows users to query every table, but with the session variablesX-Hasura-campuscheck. This means that users with this role will only be able to query information from their own campus. -
admin-campus-read-only: this role allows users to query almost all tables with a campus permission verification.
Example:
{ "campus" : { "_in" : "X-Hasura-campus" } }
-
admin: this role allows users to query any action in any table on the database. -
admin-read-only: this role allows users to query almost all tables only using theselectaction.
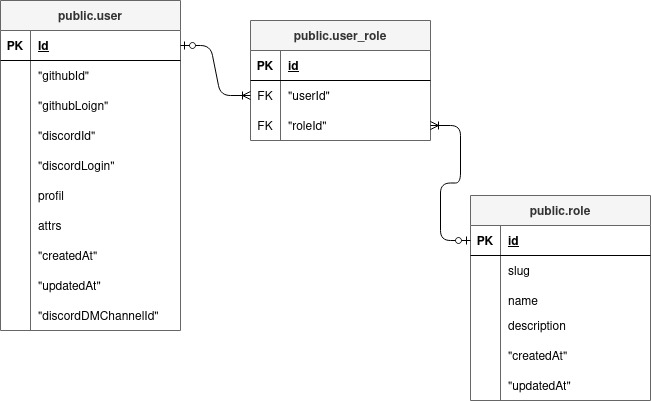
This is how the user and role tables are related to each other: